30 - 70 % of stroke patients have reduced or no use of their arm following their stroke. Shoulder pain is present in up to 84% of patients and can occur from 2 weeks to several months post stroke. The achievement of good arm position can help to prevent pain, contractures, pressure problems and respiratory complications.
Almost one in three ward patients required good arm position. The aim was for all patients unable to independently move their stroke hand to their mouth to have their arm positioned correctly.
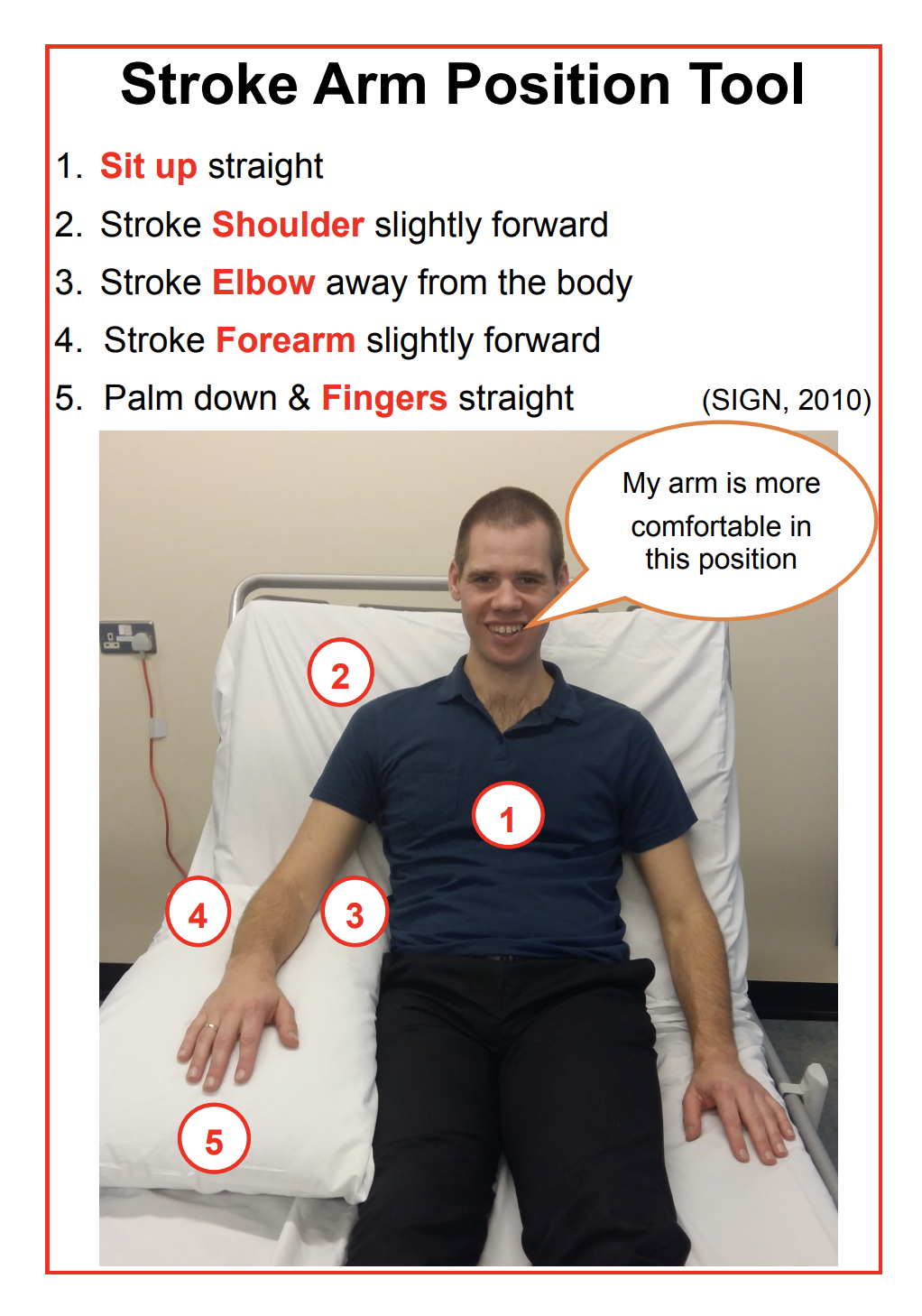
There was no clear guideline on the correct arm position. The project developed a 5 point best practice guide (see attached) developed from SIGN management of stroke guidelines (2010). The best practice guide was also used to measure the quality of the positioning being achieved. This best practice guide was used in conjunction with PDSA cycles to measure areas for improvement and measure change. The project measurement was the use of a 5 best practice guide, Yes/No scale to achieve the correct position for the patient’s stroke arm whilst in bed.
The interventions to improve the positioning of the stroke arm are:
• best practice guide above patient’s beds
• purpose education with ward staff, patients and their carers, generated by the
• the best practice guide was also placed in the ward newsletter.
• A trial of specialist positioning cushions
Almost 1 in 3 ward patients required good arm positioning and on average 3 out of 5 points were achieved, with only 41% scoring 100% (5/5). After the interventions the average score improved to 4.6 out 5, with the correct position retained for up to 2 hours.
The MDT staff had become more aware of a good arm position, with each section of the five points best practice guide being more evenly scored and 4 out of 5 points achieved. Specialist cushions might also promote better positioning of the stroke arm. The outcome of this guide has enabled an education tool and measure of the correct arm position.
Effective measures take time and effort to define and refine and are important for the direction and outcome of the project. The achievement of good arm position can help to prevent pain, contractures, pressure problems, respiratory complications and is a comfortable position.